docs
Property Mapping Rules
- Main concepts for rules: Categories
- List of available rules
- Example: Import rules
- Example: Display rules
- Example: Export rules
Main concepts for Rules
Concept: Rule categories
Rules for property mappings fall into 1 of 3 categories:
- Import Rules (Data transformation)
- Display Rules (Data validation)
- Export Rules (Data transformation)
- Each type of rule can be reordered within it’s own category, but you cannot move an export rule before an import rule
- Import rules work on the raw source data and are applied to each individual data source’s data.
-
User scriptable rules (Javascript) have access to 3 parameters, not just 1:
Parameter Description Note s The string value from the source Can be modified by previous rule rowData The entire row’s data (all the cell values, modifications, differences, etc) Cannot be modified, read-only pm The property mapping object Contains additional options such as “Is it read-only”
Concept: Order of rules
Each type of rule can be reordered within it’s own category, but you cannot move an export rule before an import rule The order that rules run in always follow the following order:
- import
- display
- export
You can reorder the rules (there are individual up/down buttons next to the header), but export rules cannot appear before import rules. Import/Export rules have an orange border, while display rules only have a gray border.
Concept: Individual sources
Import rules work on the raw source data and are applied to each individual data source’s data.
Each rule runs only on the source that it is being applied on (see image below)
Concept: Rule parameters
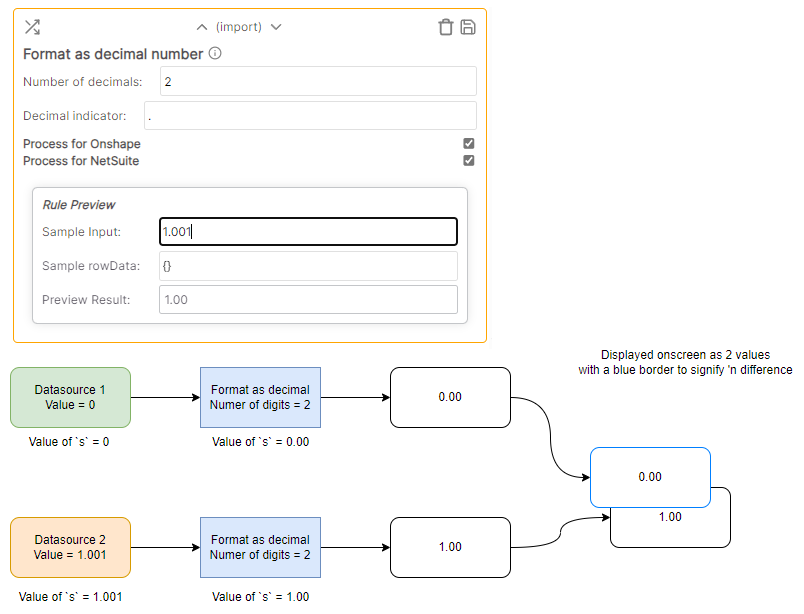
Example
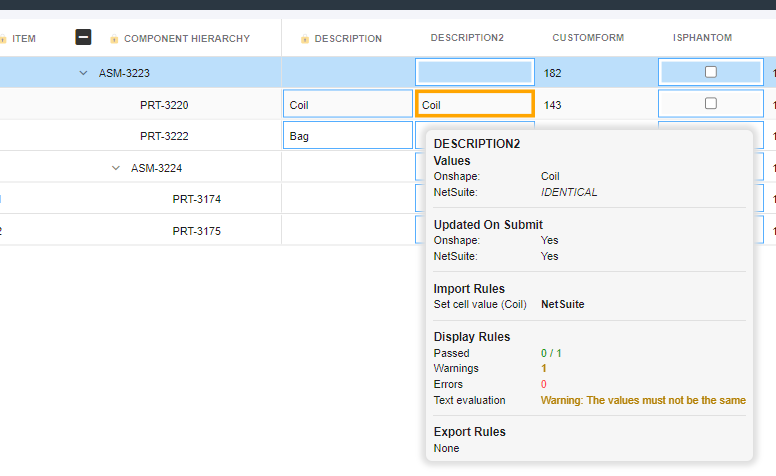
In the example below, the Format as decimal rule runs for both Onshape and NetSuite. The rule runs on the individual strings of data imported.
NOTE: The rule running for NetSuite is not aware of the data being imported from Onshape. That means that when running a rule such as a javascript Text Manipulation rule, the rule runs only for one source at a time, never for both at the same time.
The final result for both rules are overlaid in the user interface (default would be a blue rectangle)
Pro tip: One way to get around this is to create an Text evaluation rule to match the value of a cell to that of another and return a display message to the user. Or use a Text manipulation rule to write a message to a cell value and give the user a message onscreen.
For example: Let’s suppose that we have Datasource 1 (DS1) and Datasource 2 (DS2), the process would be:
Step: Setup the property mappings
- Setup the 1st property column. Give it an accessor of
descriptionwith a column mapping of propertydescriptionfor DS1 and for DS2 - Setup a 2nd property column
description2column. Give it an accessor ofdescription2. Also map it to thedescriptionproperty. - Add a
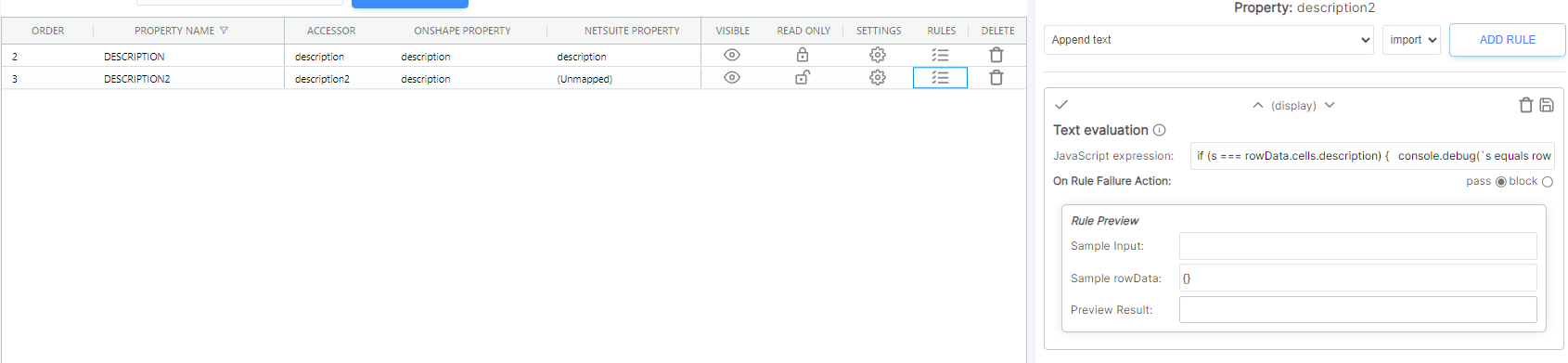
Text evaluationdisplay rule to the 2nd column.
Step: Pulling the BOM + reviewing the data
- For now let’s say the value that comes from DS1 is the value
Coil. - Enable the setting on the 2nd column:
Prefer {DS2} Value. This forces the value from DS2 to display instead of the value of DS1 displaying by default - Add a
Text evaluationrule. This rule has access to ansparameter (the current string value). Use the the following logic: - If the value of
sis equal to thedescriptionproperty, return a message to the user.
Written out in Javascript it would look like this
if (s === rowData.cells.description)
return { status: 'failure', message: `The values must not be the same` };
Note that returning any value in the message above can be customized by you.
The data from DS2 is imported after that of DS1. The rules start running for DS2
Javascript rules have access to 3 parameters, not just 1:
Typical rules only have access to the string value s which is passed to it. The Text manipulation rule has access to more data which allows for much greater scripting capability. The result of a text manipulation rule must always be a string or a representation of a string such as a javascript object which has been serialized. If it does not return a value you may experience unexpected results in the UI, possibly even instability in attempting to render client side BOMs.
| Param | Description |
|---|---|
| s | The current string value in the cell (changes with each successive import rule (if there are any) |
| rowData | The rowData object (more detail below **) |
| p | The pass / block value |
** The rowData value is a special value. It contains, but is not limited to, the following key/values:
| Key name | Description of the value |
|---|---|
| isAssemblyRow | A bool value indicating if the current row value is an assembly row (contains children according to the source) |
| componentName | The primary identifier of each row - typically the name of the component |
| componentPathArray | The path of each component. So if you have assembly A1, with Part P1, then this value will be [ 'A1', 'P1' ] |
| cells | The row values for the entire row. A typical row object might look something like this (notice the nested `cells` key): ```json { "isAssemblyRow" : false, "componentName" : "Part 1", "componentPathArray" : [ "A1", "Part 1"], "cells" : { "partNumber" : "P1", "description" : "Side plate", "revision" : "A" "material" : "steel", "qty" : 1, } } ``` |
List of Rules
| Rule name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Append Text | Import / Export | Adds the specified text to the end of the cell value |
| Calculate number | Import / Export | Uses the cell value and performs a calculation. The result of the calculation replaces the cell value |
| Export manipulation | Export only | Runs the specified javascript expression when data is exported. Has the ability to remove rowData values |
| Format as decimal | Import / Export | Converts the cell value to a number and adds the specified number of decimals. This does round the number |
| Number between | Display | The number in the cell value must be between (inclusive) the numbers specified |
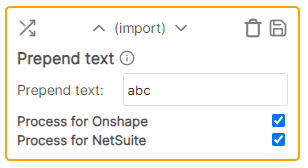
| Prepend text | Import / Export | Adds the specified text to the beginning of the cell value |
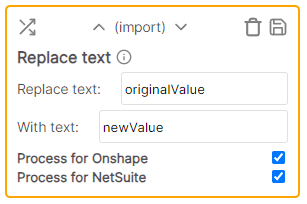
| Replace all instances | Import / Export | Replaces all instances of the specified text with the new value |
| Replace first instance | Import / Export | Replaces the first instance of the specified text with the new value |
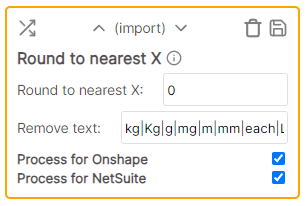
| Round to nearest X | Import / Export | Rounds the number to up or down the nearest specified digit |
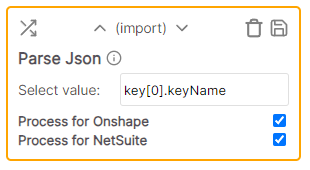
| Select from Json | Import / Export | Converts the cell value from text to a JSON object and returns the value given by the specified key |
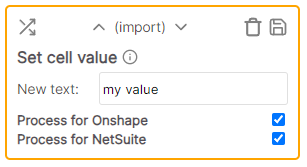
| Set cell value | Import / Export | Sets the cell value to the specified text. Existing text is replaced |
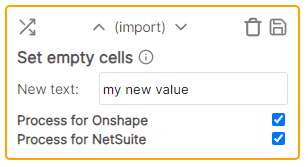
| Set empty cells | Import / Export | Set an empty (any cell that has only whitespace or no value) cell value to the specified text |
| Text contains | Display | The cell value must contain the specified text |
| Text ends with | Display | The cell value must end with the specified text |
| Text evaluation | Display | Evaluates the cell value given the JavaScript expression |
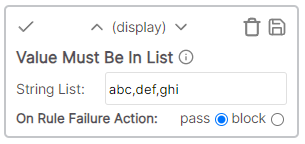
| Text is in list | Display | The cell value must be in the list of specified items (Comma separated) |
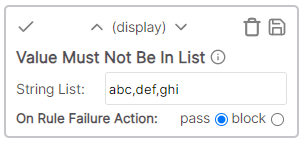
| Text is not in list | Display | The cell value must not be in the list of specified items (Comma separated) |
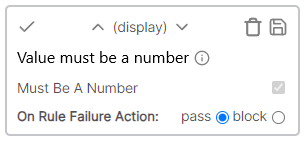
| Text is a number | Display | The cell value must not be numeric |
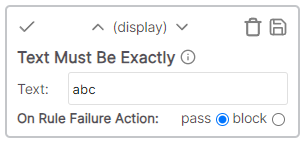
| Text is exactly | Display | The cell value must exactly match the specified text |
| Text is not a number | Display | The cell value must not be numeric |
| Text is not empty | Display | The cell value must contain text (1 or more characters) |
| Text length between | Display | The number of characters in the cell value must be between the lower and upper limit |
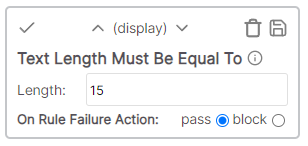
| Text length is exactly | Display | The number of characters in the cell value must be exactly the length specified |
| Text manipulation | Import / Export | Manipulates (and returns the result of) the cell value using the given the javascript expression |
| Text maximum length | Display | Limits the length of the cell value text to a maximum number of characters |
| Text minimum length | Display | The number of characters in the cell value must be greater than the specified number |
| Text not contains | Display | The cell value must not contain the specified text |
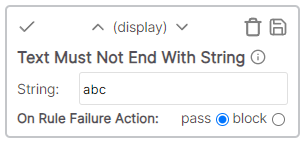
| Text not ends with | Display | The cell value text must not end with the specified text |
| Text not starts with | Display | The cell value must not start with the specified text |
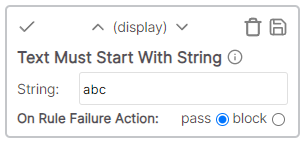
| Text starts with | Display | The cell value text must start with the specified text |
| Remove property | Import / Export | Removes the specified property when exporting the data |
Example: Import rules
Import rules are run when the data is imported from the source. The rule will change the incoming value from the datasource. For example, if you have value from a CSV file that is being imported as 0, you can transform the value using the Text Manipulation rule to change from 0 => 0.0
Example You have a value that is received from the datasource as a json object, say
{
"id" : 42,
"refName" : "Material Name"
}
You can use the
Select from Json
rule to select the key called refName from this Json object. The value displayed onscreen will be Material Name
Example
[
{
"id" : 41,
"refName" : "Material Name 1"
},
{
"id" : 42,
"refName" : "Material Name 2"
}
]
You can use the
Select from Json
rule to select the key called [1].refName from this Json object. The value displayed onscreen will be Material Name 2. The selector [1].refName uses a text string to select the value from the array of values. In this case select from the 2nd element (indexes start at 0, so select element 1, which is the 2nd element in the array of 2 elements), then select the refName key on the element. Nested properties are supported.
Example: Display Rules
Display rules are rules that trigger either warnings or errors after the data has been imported. This plays out as:
- Data is imported
- Import rules are applied to transform data
- Data is displayed onscreen
- Rules are evaluated
- Warnings or errors are displayed based on the rule conditions
A Display Rule can be set to either pass or block.
- A value of
passwill show a orange border if it fails. The user is still able to submit the BOM - A value of
blockwill show a red border if it fails. The user is not able to submit the BOM - (Colors are configurable)
Example: Export rules
Export rules are run when the data is exported from SharpSync when using the Submit BOM button. The rule will change the value sent to the datasource. For example, if you have value from a source, say Onshape, that was imported as 0, the displayed onscreen as 0.0, you can transform the value using the Text Manipulation rule to change from 0.0 => 0 so that the value may be accepted by Onshape.
Rule explanations
Below is a comprehensive list of seach Property Mapping Rule. Expand the Table of Contents and click a specific rule to jump to that rule. Learn more about Rule setup: Configure Rules
Table of Contents
Display Rules
[Cell value evaluation](#cell-value-evaluation) [Maximum text length](#maximum-text-length) [Minimum text length](#minimum-text-length) [Number between](#number-between) [Text length must be between](#text-length-must-be-between)[Interpreting the Results](#interpreting-the-results)Import/Export Rules
[Append text](#append-text) [Calculate number](#calculate-number) [Format as decimal number](#format-as-decimal-number) [Select from JSON](#select-from-json) [Prepend text](#prepend-text) [Replace text](#replace-text) [Round to nearest X](#round-to-nearest-x) [Set cell value](#set-cell-value) [Set empty cells](#set-empty-cells) [Text length must equal](#text-length-must-equal) [Text manipulation](#cell-value-manipulation) [Text must be exactly](#text-must-be-exactly) [Text must contain string](#text-must-contain-string) [Text must end with string](#text-must-end-with-string) [Text must not be empty](#text-must-not-be-empty) [Text must not contain string](#text-must-not-contain-string) [Text must not end with string](#text-must-not-end-with-string) [Text must start with string](#text-must-start-with-string) [Text must be in list](#text-must-be-in-list) [Text must not be in list](#text-must-not-be-in-list) [Text must be a number](#text-must-be-a-number) [Text must not be a number](#text-must-not-be-a-number)
Display Rules
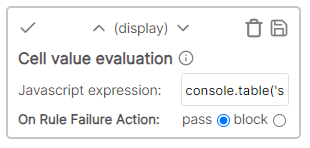
Text evaluation
Evaluates the cell value given the javascript expression. Available parameters:
- s (display value)
- rowData (the record containing the accessors data and additional metadata)
Notes on rowdata:
rowData is a object which contains the following noteworthy child items:
- rowData.cells (each cell value without modification. This can include the altered values as set in import rules)
- rowData.modifications (any modifications made by the user as at the time the rule is run)
Special notes:
Whenever you create a text evaluation rule that evaluates the value of another cell, you must take into consideration the modifications of the other cell.
e.g. if the accessor you’re evaluating for is myProperty1 and the condition is based on the value of accessor myProperty2, first check in your rule for the existance of rowData.modifications.myProperty2. If it exists, then use it, otherwise use rowData.cells.myProperty2. Example below
// if the key exists in the object return its value, otherwise, return the value in the rowData.cells
const myValue2 = "myProperty2" in rowData.modifications ? rowData.modifications.myProperty2 : rowData.cells.myProperty2;
// now do something with the value you got above
if ({conditionBasedOnMyValue2})
return { message: `the message you want to return` };
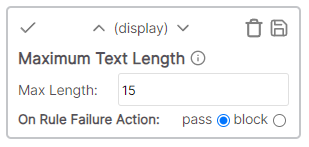
Maximum text length
Limits the length of the cell value text to a number of characters.
Example
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: 4 * Result: Fail - number of characters > rule.Minimum text length
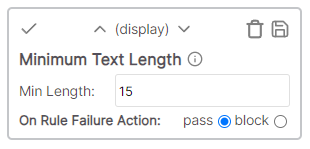
The number of characters in the cell value must be greater than the specified number.
Example
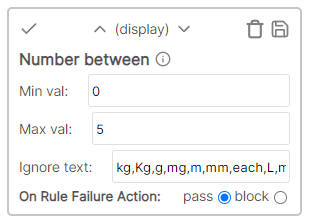
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: 4 * Result: Pass - number of characters > rule.Number between
Converts cell value to a number and evaluates if number is within a range of values, and ignores text listed in textbox.
Example
* Cell value: 12.5 kg * Rule values: * Min val: 1 * Max val: 100 * Ignore text: kg,Kg,g,mg,m,mm,each,L,ml,oz,fl * Result: Pass - "kg" ignored, cell value between min\max.Text length must be between
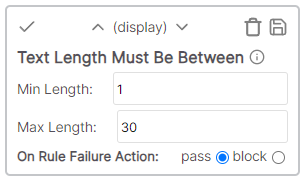
The number of characters in the cell value must be between the lower and upper limit.
Example
* Cell value: Part * Rule values: * Min length: 5 * Max length: 15 * Result: Fail - number of characters outside of min/max range.Import/Export Rules
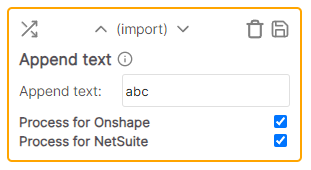
Append text
Adds the specified text to the end of the cell value.
Example
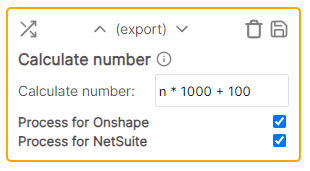
* Cell value: this * Rule value: -item (applied to all cells in column) * Result: this-itemCalculate Number
Uses the cell value and performs a calculation. The result of the calculation replaces the cell value.
Example
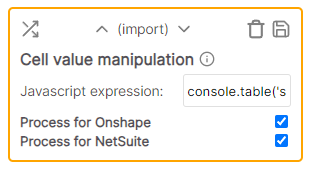
* Cell value: .07 * Rule value: n * 100 * Result: 7 (.07 * 100)Cell value manipulation
Manipulates (and returns the result of) the cell value given the javascript expression. Available parameters:
- s (original value)
- rowData (the existing row containing rowData.cells which is the accessors)
Export manipulation
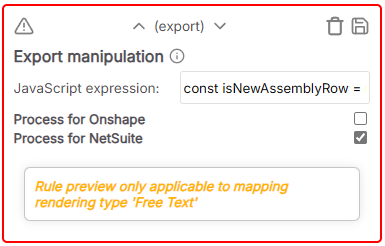
Modifies the outgoing data before it is sent to the secondary source. It is important to note 2 things:
- That there can only be 1 of these rules as it modifies all outgoing data
- That it must always return
sat the end of the statement.shere represents therowData.sourceExportDatato be modified. Failing to return it will result in corrupted data in the BOM.
e.g. given this Javascript for an isPhantom setting
const isNewAssemblyRow =
rowData.isAssemblyRow &&
rowData.isMissingInSecondaryDatasource == true &&
rowData.isFoundInSecondaryDatasource == false;
if (!isNewAssemblyRow)
{ delete s['phantomYN']; }
if (rowData.isAssemblyRow === true)
{ delete s['material']; }
return s;
Example
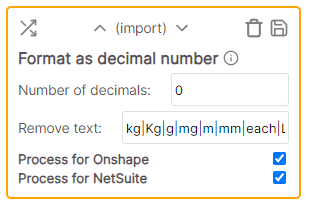
* Cell value: 12.53 m * Rule values: * Number of decimals: 4 * Remove text: kg|Kg|g|mg|m|mm|each|L|ml|oz|fl * Result: 12.5300Format as decimal number
Converts the cell value to a number and adds the specified number of decimals. This formats the number as it is viewed and does not round it. Any text specified to be removed will be replaced/ignored during the number format.
Example
* Cell value: 12.53 m * Rule values: * Number of decimals: 4 * Remove text: kg|Kg|g|mg|m|mm|each|L|ml|oz|fl * Result: 12.5300Select from JSON
Converts the cell value from text to a JSON object and returns the value given by the specified key. Supports nested key/values and arrays. You can use key.value[2].key to retrieve value for a given key.
Prepend text
Adds the specified text to the beginning of the cell value.
Example
* Cell value: 123 * Rule value: ABC- * Result: ABC-123Replace text
Replaces any instances of the specified text with the new value.
Example
* Cell value: Hello, world * Rule values: * Replace text: world * With text: there * Result: Hello, thereRound to nearest X
Rounds the number to the nearest specified number. Supports integers only. (Positive or negative whole number.)
Example
* Cell value: 1234.5678 mm * Rule values: * Round to nearest X: 10 * Ignore text: kg|Kg|g|mg|m|mm|each|L|ml|oz|fl * Result: 1230Set cell value
Sets the cell value to the specified text.
Example
* Cell value: Hello, world * Rule value: Description * Result: DescriptionSet empty cells
Set an empty (any cell that has whitespace or no value) cell value to the specified text.
Example
* Cell value is empty * Rule value: Description * Result: DescriptionText length must equal
The number of characters in the cell value must be exactly the length specified.
Example
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: 12 * Result: Fail - Description is only 11 charactersText must be exactly
The cell value must be an exact match with the specified text.
Example
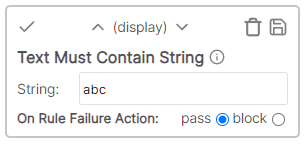
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: Description1 * Result: Fail - Description1 does not match DescriptionText must contain string
The cell value must contain the specified text.
Example
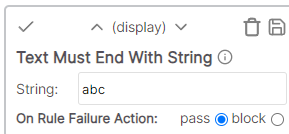
* Cell value: Final Description * Rule value: Final * Result: Pass - Cell value contains text "Final"Text must end with string
The cell value must end with the specified string.
Example
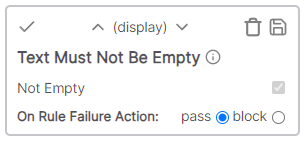
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: abc * Result: Fail - Cell value does not have suffix of abcText must not be empty
The cell value must not be empty.
Example
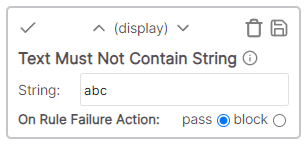
* Cell value: Description * Result: Pass - Cell value is not emptyText must not contain string
The cell value must not contain the specified string.
Example
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: rip * Result: Fail - Cell value "Description" contains "rip"Text must not end with string
The cell value must not end with the specified string.
Example
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: ion * Result: Fail - Cell value "Description" ends with "ion"Text must start with string
The cell value must start with the specified string.
Example
* Cell value: Description * Rule value: Desc * Result: Pass - Cell value "Description" begins with "Desc"Text is in list
The cell value must match a value in a string list. Entries are separated by a comma.
Example
* Cell value: Desc * Rule value: abc,def,ghi * Result: Fail - Cell value "Desc" does not match any list valueText is not in list
The cell value must not match a value in a string list. Entries are separated by a comma.
Example
* Cell value: Desc * Rule value: abc,def,ghi * Result: Pass - Cell value "Desc" does not match any list valueText must be a number
The cell value must be a number.
Example
* Cell value: 12.5a * Result: Fail - Cell value contains non-numeric character "a"Text must not be a number
The cell value must not be a number.
Example
* Cell value: 12.5a * Result: Pass - Cell value contains non-numeric character "a"Interpreting the Results
SharpSync processes and prioritizes each rule in order from top to bottom. Moving a rule up or down the list can change the result depending on the subsequent outcome. See the examples below to gain an idea of how results are evaluated:
Example 1: Text-based Rule Application
Preconditions
- Property Mapping: Description (Text)
- Sample Cell Data: “Connector Bracket 1_REL”
Rules
- Prepend Text: “ABC-“
- Text Must End with String: “_REL”
- Maximum Text Length: 25
Evaluation
- PASS: Text is appended to be “ABC-Connector Bracket 1_REL”
- PASS: Text does end with the string “_REL”
- FAIL: Text length is longer than maximum. Text was originally 23 characters; the prepended text makes the character length 27.
- Quick Fix: change the text in SharpSync by removing charcaters or abbreviating words. Datasources can be updated when the BOM is submitted with the changes, depending on the Property Mapping settings.
- If the Maximum Text Length was ordered before the Prepend Text rule, all rules would evaulate as passing.
Example 2: Numeric Rule Application
Preconditions
- Property Mapping: Weight (Numeric value)
- Sample Cell Data: “123.54 kg”
Rules
- Replace Text (removing spaces)
- Orginal Value: “ “
- New Value: “”
- Format as Decimal Number
- Number of Decimals: 0
-
Remove Text: kg KG g lb lbs
- Round to Nearest X: 1
- Number Between
- Min Value: 1
- Max Value: 123
Evaluation
- PASS: Space is removed, new text is “123.54kg”
- PASS: Text is changed to Decimal. Any characters after tenth place is dropped. New value is 123.
- PASS: Decimal is rounded to the nearest whole number of 123.
- PASS: Number is between or equal to the minimum and maximum values of 1 and 123.
- If the 2nd and 3rd rules were reversed, the last rule would fail. The number would be rounded first, which would result in the new number being 124, which is larger than the last rule’s maximum value.